Prevention of Treatment Failure

4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4227 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 293 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
HIV treatment has evolved remarkably over the years, offering individuals the opportunity to manage their condition and live long, healthy lives. However, treatment failure remains a significant concern, potentially leading to disease progression, resistance to medications, and reduced quality of life. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the causes and prevention strategies for treatment failure, empowering individuals to maintain optimal health and well-being.
Understanding Treatment Failure in HIV
Treatment failure in HIV occurs when the virus becomes resistant to the medications being used or when an individual does not adhere to their treatment plan. Resistance develops when mutations in the virus allow it to evade the effects of the medications, while non-adherence can result from various factors, including forgetfulness, side effects, or lack of access to medications. Both resistance and non-adherence can lead to increased viral load, immune system damage, and decreased quality of life.
Factors Contributing to Treatment Failure
Multiple factors can contribute to treatment failure in HIV, including:
1. Medication Resistance
*  * Viral mutations that alter the structure of the virus, making it less susceptible to medications.
* Viral mutations that alter the structure of the virus, making it less susceptible to medications.
2. Non-Adherence
*  * Failure to take medications as prescribed, including skipping doses, altering dosages, or stopping treatment altogether due to side effects, forgetfulness, or lack of access.
* Failure to take medications as prescribed, including skipping doses, altering dosages, or stopping treatment altogether due to side effects, forgetfulness, or lack of access.
3. Co-infections
*  * Infections other than HIV, such as hepatitis C, tuberculosis, or sexually transmitted infections, can interfere with HIV treatment efficacy.
* Infections other than HIV, such as hepatitis C, tuberculosis, or sexually transmitted infections, can interfere with HIV treatment efficacy.
4. Lifestyle Factors
*  * Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of treatment failure.
* Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of treatment failure.
5. Mental Health
*  * Depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can affect adherence to treatment and overall health outcomes.
* Depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can affect adherence to treatment and overall health outcomes.
6. Social Support
*  * Lack of social support, including access to healthcare, counseling, and support groups, can hinder treatment efforts.
* Lack of social support, including access to healthcare, counseling, and support groups, can hinder treatment efforts.
Prevention Strategies for Treatment Failure
Effectively preventing treatment failure in HIV requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both medication-related and non-medication-related factors. Here are key prevention strategies:
1. Optimize Medication Adherence
*  * Take medications as directed by your healthcare provider, even when you feel well. * Use medication reminders, such as alarms or phone apps. * Discuss any side effects or concerns with your provider. * Explore adherence support programs or counseling if needed.
* Take medications as directed by your healthcare provider, even when you feel well. * Use medication reminders, such as alarms or phone apps. * Discuss any side effects or concerns with your provider. * Explore adherence support programs or counseling if needed.
2. Manage Co-infections
*  * Seek prompt diagnosis and treatment for any co-infections to prevent their interference with HIV treatment. * Follow recommended screening and vaccination guidelines for common co-infections.
* Seek prompt diagnosis and treatment for any co-infections to prevent their interference with HIV treatment. * Follow recommended screening and vaccination guidelines for common co-infections.
3. Maintain Healthy Lifestyle Habits
*  * Quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and adopt a balanced diet. * Engage in regular physical activity. * Prioritize mental health by seeking support when needed.
* Quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and adopt a balanced diet. * Engage in regular physical activity. * Prioritize mental health by seeking support when needed.
4. Access Social Support
*  * Build a strong support system that includes family, friends, healthcare providers, and support groups. * Access community resources and organizations that provide assistance with housing, transportation, and other essential services.
* Build a strong support system that includes family, friends, healthcare providers, and support groups. * Access community resources and organizations that provide assistance with housing, transportation, and other essential services.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation
* 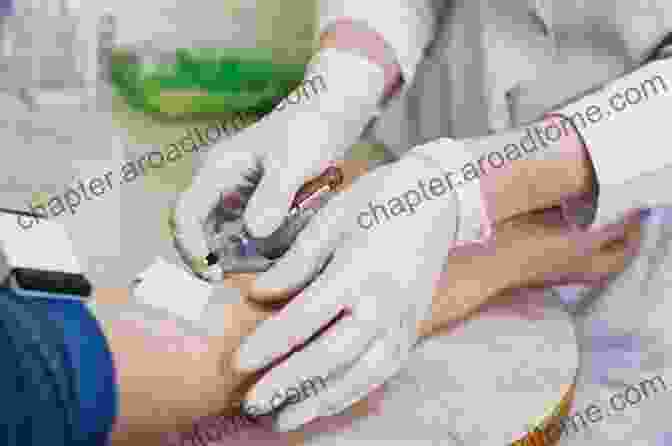 * Attend regular medical appointments for HIV monitoring. * Get viral load tests to assess treatment effectiveness. * Inform your healthcare provider about any changes in your health or adherence.
* Attend regular medical appointments for HIV monitoring. * Get viral load tests to assess treatment effectiveness. * Inform your healthcare provider about any changes in your health or adherence.
Preventing treatment failure in HIV is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being. By understanding the contributing factors and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals can increase their chances of achieving viral suppression, preserving immune function, and improving their overall health outcomes. This comprehensive guide provides valuable knowledge and guidance for individuals living with HIV, healthcare providers, and community organizations working towards the prevention of treatment failure and the empowerment of those affected by the disease.
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4227 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 293 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Michael Lewis
Michael Lewis Terri Meredith
Terri Meredith Scott West
Scott West Nancy Beaudette
Nancy Beaudette Munishwar Gulati
Munishwar Gulati Neal Allen
Neal Allen S J A Turney
S J A Turney Minna Rose
Minna Rose Nathan J Gordon
Nathan J Gordon Rawl Hardial
Rawl Hardial Nicola Hall
Nicola Hall Michael S Nystul
Michael S Nystul Michael Dauphinais
Michael Dauphinais Sara E Gorman
Sara E Gorman Nate Ciraulo
Nate Ciraulo Sri Ram Kaa
Sri Ram Kaa Nancy Congleton
Nancy Congleton Nancy Marchant
Nancy Marchant Penelope Rowlands
Penelope Rowlands Sandra Kent
Sandra Kent
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Jarrett BlairBreak the Chains of Chronic Back Pain: A Comprehensive Guide to Healing and...
Jarrett BlairBreak the Chains of Chronic Back Pain: A Comprehensive Guide to Healing and... Martin CoxFollow ·8.1k
Martin CoxFollow ·8.1k Mario SimmonsFollow ·19.7k
Mario SimmonsFollow ·19.7k Ian MitchellFollow ·4.3k
Ian MitchellFollow ·4.3k Bryan GrayFollow ·9.9k
Bryan GrayFollow ·9.9k Jon ReedFollow ·19.4k
Jon ReedFollow ·19.4k Randy HayesFollow ·7.8k
Randy HayesFollow ·7.8k Joshua ReedFollow ·4.9k
Joshua ReedFollow ·4.9k Diego BlairFollow ·8.6k
Diego BlairFollow ·8.6k

 Samuel Beckett
Samuel BeckettPortrait of the Plague Doctor: A Chilling Tale of Fear...
Prologue: A...

 Elliott Carter
Elliott CarterTrends in Modeling and Simulation Studies in...
Unveiling the Convergence of...

 Natsume Sōseki
Natsume SōsekiCells For Kids: Science For Children
Unlock the Microscopic...

 Anthony Wells
Anthony WellsUnlock the Power of Understanding: Embrace the African...
Embark on a Journey of Truth,...
 Forrest Reed
Forrest ReedBreaking Free: Healing from Toxic Relationships Between...
Are you struggling...
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4227 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 293 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |